Efficient Rapid Sheet Metal Prototyping Services
Precision Sheet Metal Solutions: From Prototype to Production
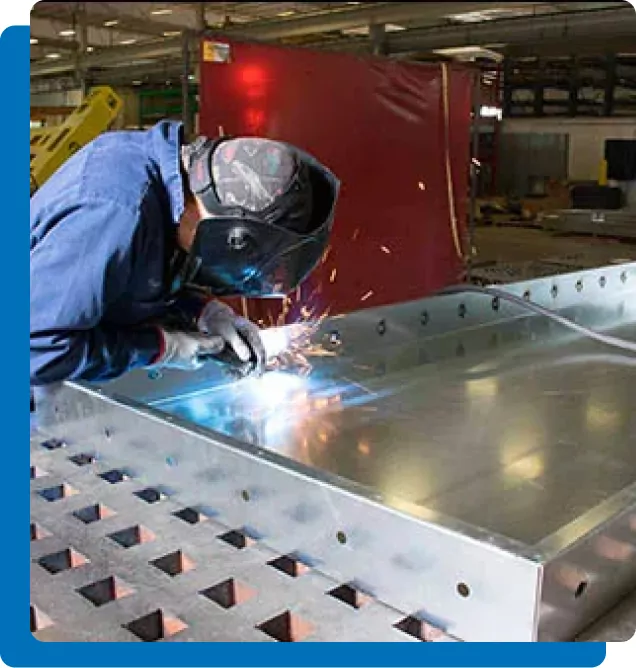


Key Benefits of Sheet Metal Fabrication
Sheet metal fabrication is a versatile and reliable manufacturing process that offers numerous advantages across various industries. Here are some of the key benefits:
High Strength and Durability
Sheet metal components are known for their exceptional strength and durability. The process allows for the creation of robust parts that can withstand harsh conditions, making them ideal for applications in automotive, aerospace, and industrial settings.
2Precision and Customization
Sheet metal fabrication enables high levels of precision and customization. Whether it's a simple prototype or a complex, multi-part assembly, the process can be tailored to meet exact specifications, ensuring that each component fits perfectly within the overall design.
3.Cost-Effective for Both Low and High Volume Production
The flexibility of sheet metal fabrication makes it cost-effective for both small-scale prototyping and large-scale production runs. Economies of scale can be achieved with minimal tooling costs, making it an attractive option for a wide range of projects.
4.Wide Material and Finish Options
Sheet metal fabrication offers a vast array of material choices, including steel, aluminum, brass, and stainless steel, each with unique properties suitable for different applications. Additionally, various finishes such as powder coating, plating, and painting can enhance the appearance and corrosion resistance of the final product.
5 .Versatility in Design and Function
The process supports a wide range of design possibilities, from simple flat parts to complex 3D structures. This versatility allows for the creation of functional components that can be easily integrated into larger systems, making sheet metal fabrication a go-to choice for engineers and designers.
6. Rapid Prototyping and Iteration
Sheet metal fabrication allows for quick turnaround times in prototyping, enabling faster design iterations and quicker time-to-market. This is particularly beneficial in industries where innovation and speed are critical, such as electronics and robotics.
7 .Sustainability and Recyclability
Many sheet metals are recyclable, making this fabrication process environmentally friendly. The ability to reuse materials and minimize waste contributes to sustainable manufacturing practices.
8 .Ease of Assembly and Integration
Sheet metal parts can be designed with features that facilitate easy assembly and integration with other components. This reduces the complexity and cost of final assembly, ensuring smoother production workflows.
Common Sheet Metal Applications
- Appliances
- Chassis
- Fuselages
- Body panels
- Doors
- Kitchen equipment
- Brackets
- Enclosures
- Office equipment

Understanding Sheet Metal Fabrication: A Comprehensive Guide
Sheet metal fabrication is a versatile manufacturing technique that involves transforming sheet metal into functional parts through various processes. The thickness of sheet metal typically ranges from 0.006 to 0.25 inches (0.015 to 0.635 centimeters), making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
The processes involved in sheet metal fabrication include cutting, bending, and punching. These processes can be used independently or in combination to achieve the desired shape and functionality of the part. Cutting involves separating the metal into specific shapes, while bending forms the metal into the required angles. Punching, on the other hand, creates holes or patterns in the metal.
Sheet metal fabrication is used to create both functional prototypes and end-use parts. However, end-use parts often require additional finishing processes, such as painting, plating, or powder coating, to enhance their appearance and durability before they are ready for market. This comprehensive approach ensures that the final product meets the highest standards of quality and performance.
The Mechanics of Sheet Metal Fabrication: A Step-by-Step Overview
Why Thin Metal Sheets Are Ideal for Fabrication
The Three Core Categories of Fabrication Processes:
Cutting Sheet Metal to Shape
Material removal is a fundamental process in sheet metal fabrication, where the metal is precisely cut into desired shapes and sizes. This involves using various cutting techniques such as shearing, laser cutting, water jet cutting, and plasma cutting. Each method offers unique advantages, from the precision of laser cutting to the versatility of water jet cutting. By removing excess material, the sheet metal can be tailored to fit specific design requirements, forming the basis for further fabrication steps.
Shaping Sheet Metal through Bending and Forming
Material deformation is a critical process in sheet metal fabrication, where the metal is bent or formed into specific shapes without removing any material. This is typically achieved through processes such as: Bending: Using press brakes or other bending tools, sheet metal is bent to precise angles. This process is essential for creating structural components and enclosures. Forming: Techniques like rolling, stamping, and deep drawing are used to transform flat sheets into complex three-dimensional shapes. Forming allows for the creation of intricate parts with high accuracy and repeatability.
Joining Sheet Metal Components
Material assembly is a vital phase in sheet metal fabrication, where individual metal parts are joined together to form a complete structure. This process involves several techniques, each chosen based on the specific requirements of the project Material assembly ensures that all fabricated parts are securely and accurately joined, resulting in a functional and robust final product. Whether for structural integrity or aesthetic appeal, the right assembly technique is crucial for achieving the desired outcome in any sheet metal project.
Sheet Metal FAQ's
- Laser Cutting: Ideal for high precision and intricate designs. It works well with a variety of materials, including stainless steel, aluminum, and carbon steel. Laser cutting is suitable for thin to medium gauge sheets and offers tight tolerances and fast lead times.
- Water Jet Cutting: Known for its versatility and ability to cut through thick materials without generating heat-affected zones. It is suitable for metals, composites, and even some non-metallic materials. Water jet cutting is ideal for thicker sheets and applications where heat-sensitive materials are involved.
- Plasma Cutting: Best suited for cutting electrically conductive materials like steel, aluminum, and copper. It is efficient for thicker sheets and offers faster cutting speeds compared to laser cutting. Plasma cutting is ideal for industrial applications where high productivity is required.
We offer complete flexibility when it comes to order quantities. Whether you need a single prototype to test a new design or a large production run of 1,000+ units, we can accommodate your needs. There is no minimum order quantity, ensuring that you can get exactly what you need, when you need it.



Put your parts
into production today
All information and uploads are secure and confidential.
